Throat Diseases and Doctors: Importance of Healthcare in Refugee Resettlement
Category : | Sub Category : Posted on 2024-10-05 22:25:23
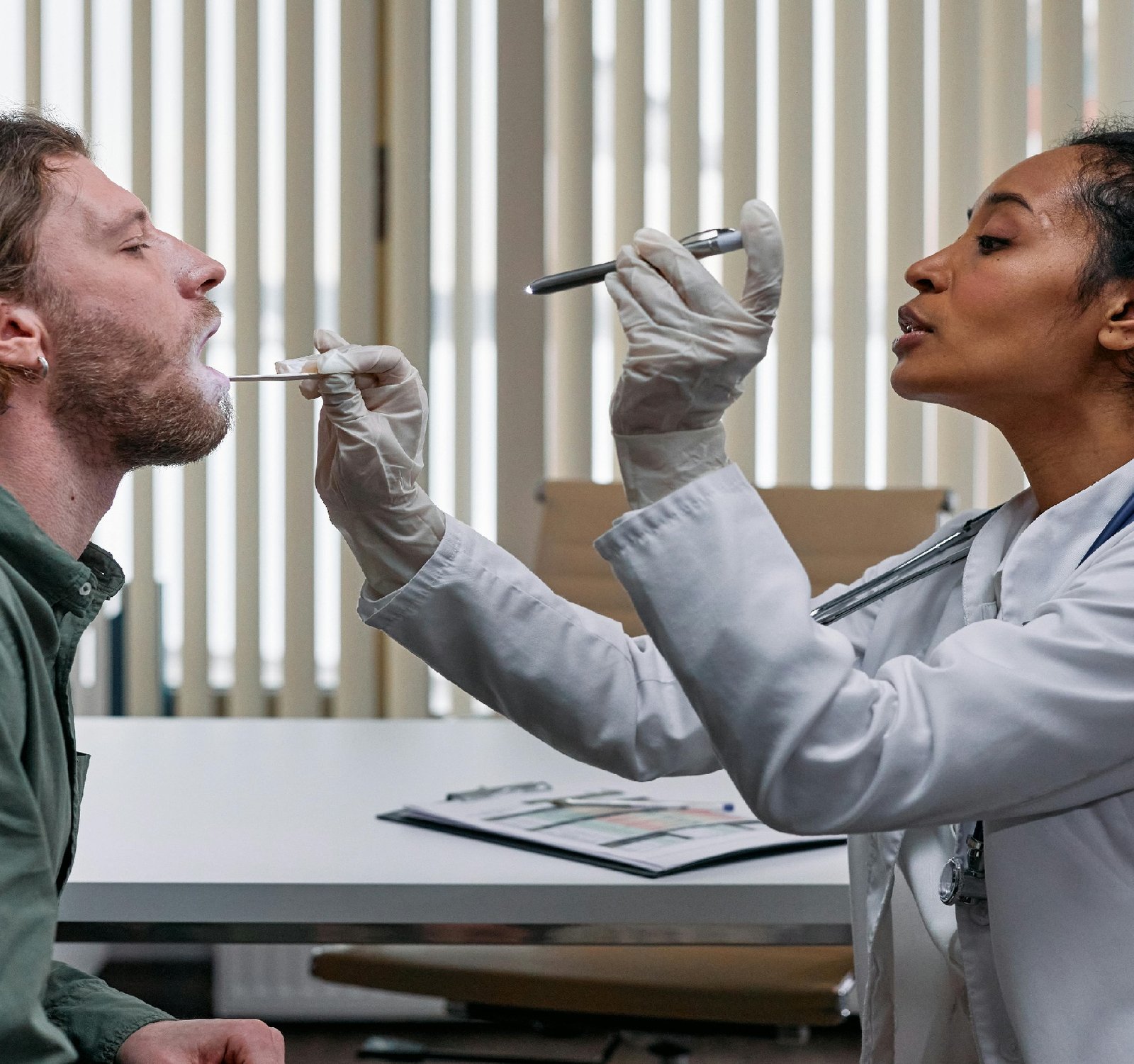
Refugee resettlement is a complex and challenging process that involves providing essential services, including healthcare, to individuals and families who have been forced to flee their homes due to various reasons such as conflict, persecution, or natural disasters. Among the many healthcare concerns that refugees face, throat diseases can be particularly problematic and may require specialized care from doctors. Throat diseases encompass a range of conditions that affect the throat, such as sore throat, tonsillitis, laryngitis, and more serious conditions like throat cancer. These illnesses can be caused by viral or bacterial infections, environmental factors, or underlying health conditions. For refugees who may have experienced trauma, poor living conditions, malnutrition, or lack of access to healthcare in their home countries, the risk of developing throat diseases is heightened. In the context of refugee resettlement, providing access to healthcare services, including adequate treatment for throat diseases, is crucial for ensuring the well-being of individuals and families. Doctors play a key role in diagnosing, treating, and managing throat diseases in refugees. They have the expertise to identify the underlying causes of throat symptoms, prescribe appropriate medications, recommend lifestyle changes, and refer patients to specialists if needed. Doctors working with refugees must be culturally competent, sensitive to the unique challenges faced by this population, and able to provide care in a compassionate and respectful manner. Language barriers, trauma-related issues, and cultural beliefs can all impact the healthcare experiences of refugees, making it essential for doctors to approach each patient with understanding and empathy. In refugee resettlement settings, healthcare providers often work in multidisciplinary teams that include medical professionals, mental health specialists, social workers, and interpreters. This collaborative approach ensures that refugees receive comprehensive care that addresses their physical, mental, and social needs – all of which are interconnected and crucial for their successful integration into their new communities. Efforts to improve healthcare for refugees with throat diseases should also include preventative measures, such as promoting proper hygiene practices, providing vaccinations, and offering health education sessions on how to recognize symptoms and seek medical help when needed. By taking a proactive approach to healthcare, doctors and healthcare organizations can help prevent the spread of throat diseases and improve the overall health outcomes of refugees. In conclusion, throat diseases are a significant health concern for refugees during the resettlement process. By prioritizing access to healthcare services and ensuring that doctors have the resources and support they need to provide high-quality care, we can help alleviate the burden of throat diseases on refugees and support their health and well-being as they build new lives in their host countries. Healthcare professionals, policymakers, and communities all have a role to play in creating inclusive and supportive healthcare systems that meet the diverse needs of refugees.
https://garganta.org
https://ciego.org
https://enferma.org
https://oreilles.org
Leave a Comment:
SEARCH
Recent News
- Zurich, Switzerland has long been known for its exceptional quality of life, beautiful surroundings, and high standard of healthcare. In contrast, the Russian healthcare system has faced various challenges and struggles over the years. Let's delve into the differences between the healthcare systems in Zurich, Switzerland, and Russia.
- Navigating Medical Device Regulations in Zurich, Switzerland
- In the bustling city of Zurich, Switzerland, finding healthy fast food options can be a challenge. However, with a little exploration and curiosity, you can discover some fantastic spots that offer nutritious and delicious meals on the go.
- YouTube Content Creation: Exploring the Russian Healthcare System
- In today's digital age, YouTube has become a powerful platform for content creators to share their knowledge and expertise with a global audience. One particular niche that has been gaining traction on YouTube is the creation and translation of content related to medical devices regulation.
- Are you looking for tips on creating YouTube content about healthy fast food options and the importance of translation in reaching a wider audience? Let's dive into how you can combine these two aspects to create engaging and informative videos for your channel.
- Exploring the Russian Healthcare System: Insights from a YouTube Channel
- Navigating the Regulatory Landscape for Medical Devices on YouTube
READ MORE
3 months ago Category :

Zurich, Switzerland has long been known for its exceptional quality of life, beautiful surroundings, and high standard of healthcare. In contrast, the Russian healthcare system has faced various challenges and struggles over the years. Let's delve into the differences between the healthcare systems in Zurich, Switzerland, and Russia.
Read More →3 months ago Category :

Navigating Medical Device Regulations in Zurich, Switzerland
Read More →3 months ago Category :

In the bustling city of Zurich, Switzerland, finding healthy fast food options can be a challenge. However, with a little exploration and curiosity, you can discover some fantastic spots that offer nutritious and delicious meals on the go.
Read More →3 months ago Category :
