When discussing throat infections in relation to the Chinese language, it is important to understand the impact that these infections can have on one's ability to communicate effectively. The throat plays a crucial role in speech production, and when it becomes infected, it can lead to various challenges in speaking and even in pronouncing certain sounds in the Chinese language.
Category : | Sub Category : Posted on 2024-10-05 22:25:23
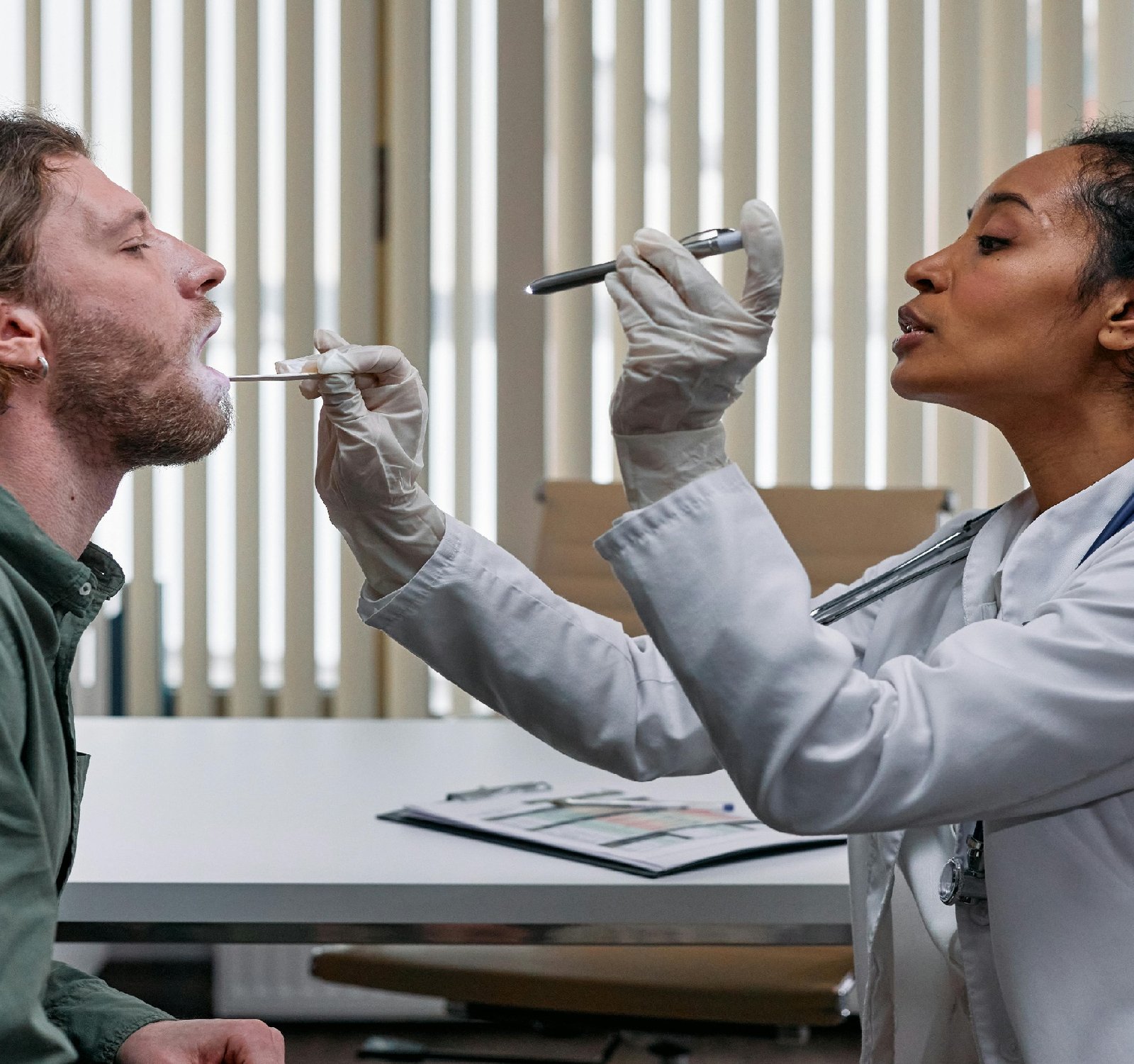
Throat infections, such as pharyngitis or laryngitis, can cause symptoms like sore throat, hoarseness, and difficulty swallowing. In the context of speaking Chinese, a sore throat can make it uncomfortable to produce the tones and sounds necessary for clear communication. The tonal nature of Chinese means that even slight changes in pronunciation can alter the meaning of a word, so maintaining clarity is essential. For individuals learning Chinese as a second language, throat infections can pose additional challenges. Pronunciation in Chinese can already be difficult for beginners due to the presence of tones and unfamiliar sounds. When a throat infection is added into the mix, the task becomes even more arduous. Students may struggle to be understood or to differentiate between similar-sounding words, leading to frustration and slower progress in language acquisition. In Chinese culture, maintaining harmony and respect in communication is highly valued, and clear speech is seen as a reflection of one's education and social status. Therefore, individuals suffering from throat infections may feel self-conscious about their speech impediments, especially in formal or professional settings. To mitigate the impact of throat infections on speaking Chinese, individuals can take steps to prevent these infections in the first place. This includes practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, and avoiding irritants like smoking or excessive yelling. In cases where a throat infection does occur, seeking prompt medical treatment and resting the voice are crucial for recovery. In conclusion, throat infections can present challenges for individuals speaking the Chinese language, affecting their ability to communicate clearly and effectively. By understanding the impact of these infections and taking steps to prevent and address them, individuals can maintain their linguistic abilities and continue to engage meaningfully in Chinese communication.
https://garganta.org
Leave a Comment:
SEARCH
Recent News
- Zurich, Switzerland has long been known for its exceptional quality of life, beautiful surroundings, and high standard of healthcare. In contrast, the Russian healthcare system has faced various challenges and struggles over the years. Let's delve into the differences between the healthcare systems in Zurich, Switzerland, and Russia.
- Navigating Medical Device Regulations in Zurich, Switzerland
- In the bustling city of Zurich, Switzerland, finding healthy fast food options can be a challenge. However, with a little exploration and curiosity, you can discover some fantastic spots that offer nutritious and delicious meals on the go.
- YouTube Content Creation: Exploring the Russian Healthcare System
- In today's digital age, YouTube has become a powerful platform for content creators to share their knowledge and expertise with a global audience. One particular niche that has been gaining traction on YouTube is the creation and translation of content related to medical devices regulation.
- Are you looking for tips on creating YouTube content about healthy fast food options and the importance of translation in reaching a wider audience? Let's dive into how you can combine these two aspects to create engaging and informative videos for your channel.
- Exploring the Russian Healthcare System: Insights from a YouTube Channel
- Navigating the Regulatory Landscape for Medical Devices on YouTube
READ MORE
3 months ago Category :

Zurich, Switzerland has long been known for its exceptional quality of life, beautiful surroundings, and high standard of healthcare. In contrast, the Russian healthcare system has faced various challenges and struggles over the years. Let's delve into the differences between the healthcare systems in Zurich, Switzerland, and Russia.
Read More →3 months ago Category :

Navigating Medical Device Regulations in Zurich, Switzerland
Read More →3 months ago Category :

In the bustling city of Zurich, Switzerland, finding healthy fast food options can be a challenge. However, with a little exploration and curiosity, you can discover some fantastic spots that offer nutritious and delicious meals on the go.
Read More →3 months ago Category :
